No wake zones aren’t just suggestions – they are critical for the safety and preservation of Michigan’s marine environment.
By following no wake zone laws, you are not only protecting people – you are helping aquatic ecosystems thrive.
In this quick guide, we’ll break down what no wake zones are and why they need to be respected (from a legal, safety, and conservation standpoint).
What is a No Wake Zone?
In Michigan, a “no wake zone” refers to a regulation put in place to protect shorelines, swimmers, small boats and docks.
For those new to boating or unfamiliar with boating terminology, boats give off a wave as they move through the water. This wave is known as wake.
Wake is regulated for safety and environmental reasons. You can think of a no wake zone almost the same as a 25 or 15 mph speed limit in a neighborhood – a requirement to travel at a speed that is safe, slow, and controlled.
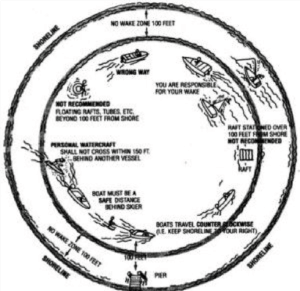
Put simply: A no wake zone is an area in a body of water – typically close to shorelines and structures – where boats must travel at idle speed to avoid creating wake.
Why They’re Legally Important
No wake zones aren’t just community guidelines or agreed upon rules. No wake zones are included in both state and local laws – requiring you to abide or face the legal repercussions.
State regulations (Michigan): Michigan state legislature provides a baseline for no wake zone laws. In Michigan, it is required that all boats travel at slow, no wake speeds within 100 feet** of:
- Shorelines
- Moored or anchored vessels
- Docks or rafts
- Marked swimming areas or individuals in the water
**100 ft is measured from the nearest object. If an anchored boat is 20 feet from shore, you must not create a wake within 100 feet from that boat (120 ft from the shore).
Personal watercraft (PWC’s) like jet skis are regulated even more strictly than normal boats and are not allowed to produce wake within 200 feet of Great Lakes shorelines. Expect an upcoming blog post discussing the importance of safe and legal operation of personal watercraft!
Local regulations (vary based on location): In addition to the state laws surrounding no wake zones, some counties have specific rules about where wake cannot be produced. It is always wise to check for any county specific rules and regulations before taking your boat somewhere new.
Michigan DNR’s website has a page that lists the local controls (local rules) for the bodies of water within each of Michigan’s counties. This is a great resource for any boater looking to explore Michigan’s waterways safely and legally.
Legal Consequences: If you break state or local no wake zone laws, the punishments are steep. Firstly, not respecting a no wake zone can land you a civil infraction with a fine of up to $500. There are no specified increased penalties for subsequent violations.
If your wake happens to injure someone in the water or cause property damage, the outlook changes completely. For starters, if another person or someone’s property is damaged as the result of the wake you created, the civil infraction you normally receive for a no wake violation gets graduated to reckless operation – a misdemeanor. If you are found guilty of reckless operation, you may be prohibited from operating a water vessel for up to 2 years and have to complete a marine safety educational program. You also may be held liable for any medical expenses and property damage that you caused (civil liability).
Reasons for No Wake Zones
You may be left wondering, “What is the purpose of no wake zones?” The answer to this question is multifaceted – here are the main reasons:
Safety of People in the Water:
- Swimmers, paddleboarders, kayakers, and anglers often occupy shallow, near-shore areas.
- Wake can injure people in or near the water.
- Wake can cause smaller boats to take on water (sinking hazard) or get pushed around (hazard to swimmers).
- Slow speeds near shore help prevent injury and collisions in high traffic areas.
Protection of Shorelines & Environmental Conservation:
- Wake can cause erosion to natural shorelines which is extremely costly and frustrating for property owners.
- Wake disturbs sensitive aquatic habitats, including wetlands, spawning areas, and nesting grounds.
- Wake can disrupt sediment, clouding the water and harming fish and plant life.
Minimizing Damage to Moored Vessels & Docks:
- Boats tied to docks or anchored in marinas can be slammed against pilings or other boats due to excessive wake.
- Wake can cause damage to man-made seawalls, docks, and retaining walls.
- Slow speeds near shore help prevent damage like the examples above.
What You Can Do
In order to operate a boat safely and responsibly, make sure you abide by no wake zone laws. By respecting no wake zones, you are doing a service to other water users, to property owners, and to the body of water itself. By going slow around shorelines, you are ensuring that the aquatic ecosystem you are enjoying is safe, accessible, and beautiful for years to come.
Get David Get Paid
If you or a loved one were injured or suffered property damage as the result of a negligent boater creating an illegal wake, make sure you reach out to Femminineo Law today. The team here at Femminineo Law is highly knowledgeable of all the intricacies of Michigan marine law. We can confidently help you back to your feet following a swimming or boating accident.
Give us a call at 855-65-CRASH or visit our website at getdavidgetpaid.com, today!
Get David, Get Paid.


